Table of contents
In today’s world, cloud computing has become an integral part of businesses and organizations. It provides numerous benefits, including scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Load Balancer are foundational for modern cloud architectures, solving real-world problems like handling failures, optimizing routing, and ensuring security.
Understanding load balancers is crucial to avoid critical incidents, as seen in the Atlassian Confluence case where improper load balancer configurations impacted service availability, highlighting that no one is immune.
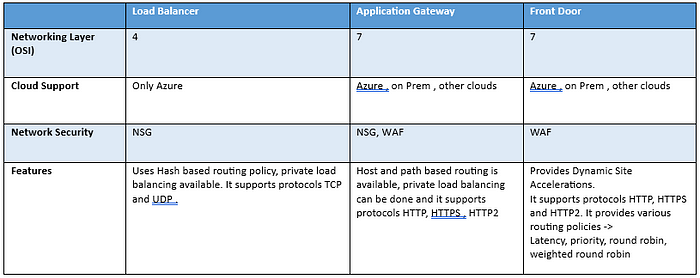
The term load balancing refers to networking solution used to distribute traffic across multiple servers or computing resources. It provides benefits like optimize resources, improve application availability, minimize response time & maximize throughput etc. In this blog, we will have a look into the different load balancing feature at different layers of networking for which the Azure provides us different load balancers.
This blog extracts the essence of effective usage of load balancers related to DevOps.
What is a load balancer ?
Load Balancer are used to disturbed the traffic when its low / heavy accordingly to the backend servers (VM) or Resources.
It occupies layer 4 (Transport) in OSI model and 3 in TCP/IP model.
Load Balancers provide security using virtual network and firewalls.
Two major load balancers are available :
1. public -> Internet facing
2. private -> On Prem hybrid connections
Load balancing capabilities provided by Azure
The following table provides a simplified view of the the load balancing option provided by the Azure.
Usage of Traffic Manager in load balancing
When a application is public facing , based on metrics like discounts on sale, popularity and festival the application will be hit with higher frequency and the number of request to the application will be increasing based on the usage which is termed as traffic.
When the Traffic is heavy there are possibilities of
Delay in loading application
Improper working of application functionality
Refresh latencies would affect the money transaction as well.
So ultimately it will lead to the loss in business .
Inorder to avoid this Azure provides us Traffic Manager with capability to reroute the traffic / requests into load balancers with various routing techniques based on
Geographical, latency, weighted, priority, subnet and multi-valued.
Traffic Manager is a DNS-based traffic load balancer. This service allows you to distribute traffic to your public facing applications across the global Azure regions. It uses DNS to route client request to various endpoints and also provides health monitoring for all endpoints.
Use-case Architecture to choose the right load balancing option in DevOps
1. Load Balancer
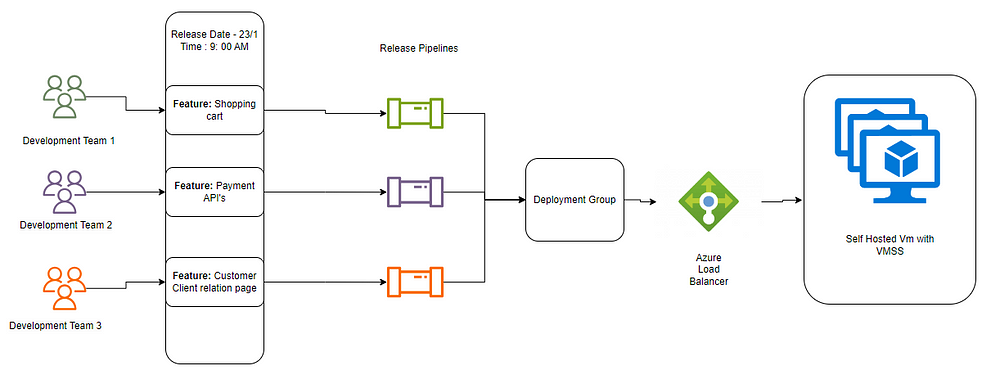
Load Balancer can be used against the Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS) to balance and it directly depends the number of self hosted runner used under deployments.
During Development , multiple teams can run multiple deployments at a time in that case if there is a singe self hosted vm then there runner will be in waiting mode for long which will increase the development teams. so in-order to avoid it based on the necessity its good practice to increase the VMSS for the demand and smoothly run the deployment.
The VMSS can be used in Azure Devops pipelines along with Azure Deployment Groups to facilitates the demand.
Azure Load Balancer is a high-performance, low-latency Layer 4 load-balancing service (inbound and outbound) for all UDP and TCP protocols. It is zone-redundant, ensuring high availability across Availability Zones and handle millions of requests per second.
Use Case:
Considering there are three different development team which are development different functionality which are with different programming languages and frameworks, they have a deployment on same day to make all the feature to work coherently. In Order to do that the Self hosted Vm should balance the load and provision similar vms .
2. Application Gateway
Azure Application Gateway is a web traffic load balancer that enables you to manage traffic to your web applications. It's a Layer 7 load balancer and can do routing based on request URL. For example, if website request for /pdf and /images these can be routed to two different server pools configured for each type.
Application Gateway is used in the (Layer 7) which used to handle the data at Application layer (Http/Https/Http2).
This will be used to reroute the traffics to application layered resources in Azure like Azure Apim Management / it can provision VM’s for a set users using application gateway for containers.
Use Case:
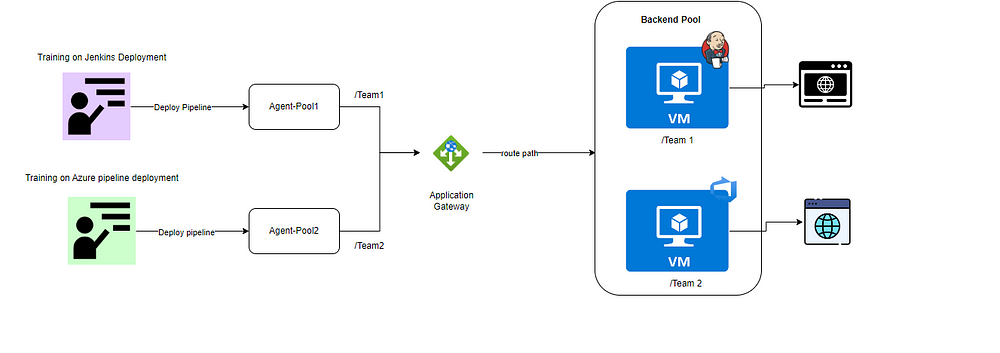
Create a VMs for the training teams A and B , with two VMs .
VM1 :-
Jenkins training will be given.
When team1 runs the pipeline build and deployment should happen in vm1.
VM2 :-
ADO pipelines training will be given.
When team2 runs the deployment should happen in vm2.
As a DevOps engineer provision VMs for both these teams mentor which will be helpful to train the students.
3. Azure Front Door
Azure Front Door uses Point of Presence as a underlying mechanism in provisioning the necessary data in minutes . its a combination of security and Content Delivery networks. Azure Front Door also opens up facilities to connect to onPrem and azure based resource data to be fetched ., so it opens a Hybrid solution.
It can be effectively used in Banking and Media Industries.
Front Door is an application delivery network that provides global load balancing and site acceleration service for web applications. It's a Layer 7 load balancer providing feature like SSL offload, path-based routing, caching, etc. to improve performance and high-availability of your applications.
Use Case:
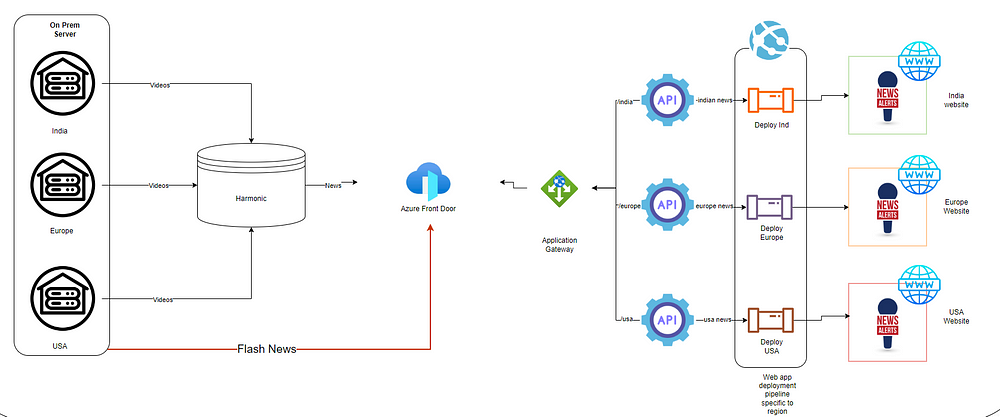
There is a global news channel which needs its website to be updated with latest news videos from each region .
The videos are stored in the harmonics account. Now you to fetch the videos into your website securely and deploy them into your web app on daily basis.
Conclusion:
I have explained the load balancing importance and the resources which Azure offers to manage load balancing with respect to deployment strategies with DevOps given a simplified examples.
In real world mostly load balancer and application gateway is used widely.
Azure Front has extensible features which focuses on CDN.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/guide/technology-choices/load-balancing-overview